If you’re considering a solar installation for your home or facility, you may want to consider learning about measuring solar radiation. Why is this important? Because the design of your solar system (type and quantity of PV panels, etc.) is affected by the amount of sunlight present in the location of your installation at a given time.
In this article, we take a look at solar radiation, global solar radiation and the methods to measure solar radiation.
What is solar radiation?
Solar radiation is often defined as the energy reaching the earth from the sun. A large part of this is visible sunlight, but the solar spectrum extends into the UV as well as the near infra-red.
Solar radiation reaches us in different ways: directly from the sun (direct solar radiation), through scattering through the atmosphere (diffuse solar radiation) or via reflections. These quantities can be measured separately, but most of the times people are interested in the total radiation on the surface: the global horizontal irradiance.
What is global solar radiation?
Our sun outputs radiation over wavelengths from 0.15 to 4.0 µm, which is called the solar spectrum. The measurement of the sun’s radiation on the earth is referred to as global solar radiation. Sometimes called short-wave radiation, global solar radiation is both the direct and diffuse solar radiation received from the hemisphere.
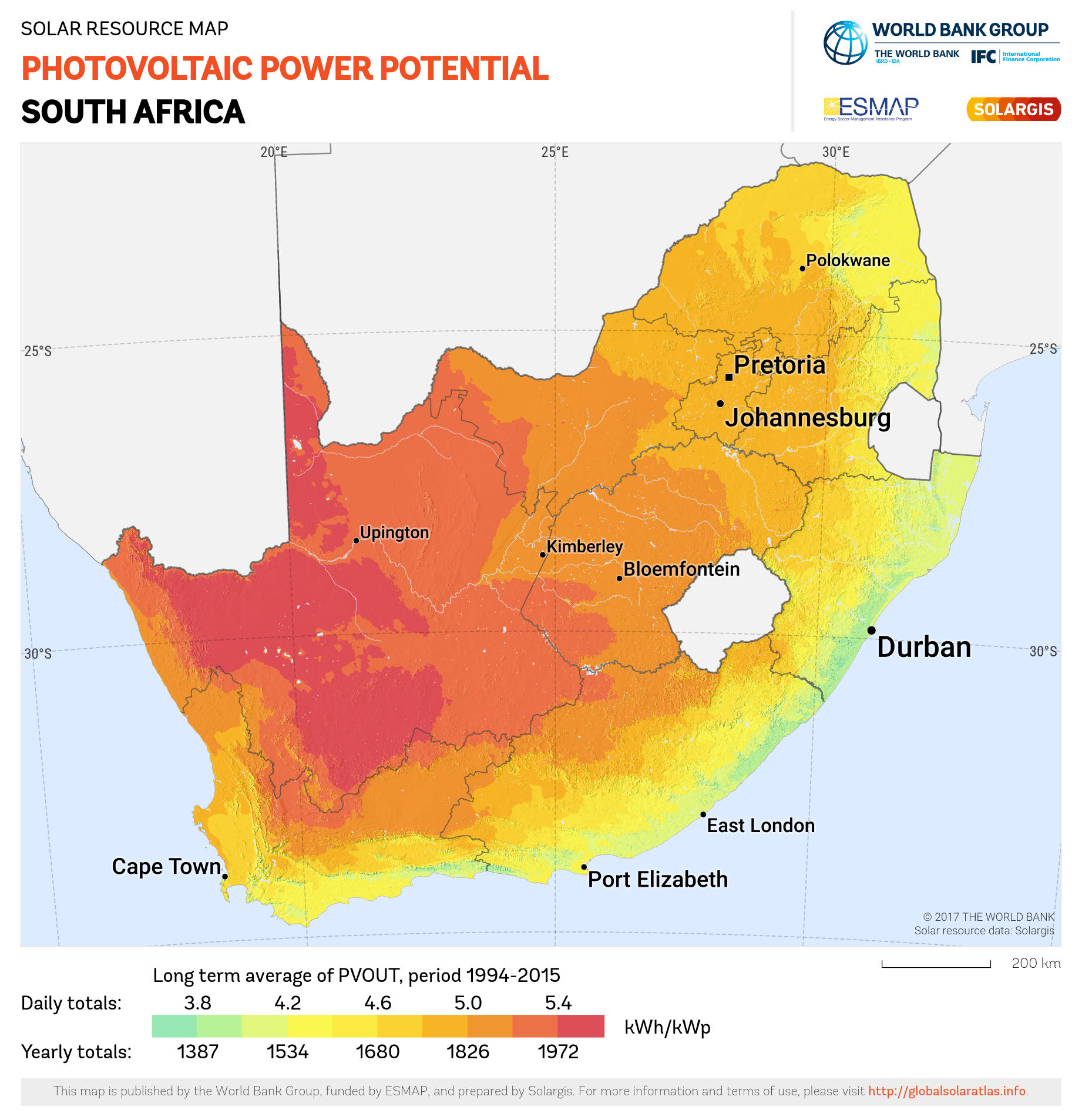
While solar radiation is the amount of radiant energy emitted by the sun, solar irradiation refers to the amount of solar radiation received from the sun per unit area which is expressed in kW/m². The below image depicts the solar irradiance map of South Africa.
What are the methods to measure solar radiation?
The two common methods which characterise solar radiation are the solar radiance (or radiation) and solar insolation.
1. Solar Radiance
The solar radiance is an instantaneous power density in units of kW/m2. The solar radiance varies throughout the day from 0 kW/m2 at night to a maximum of about 1 kW/m2. The solar radiance is strongly dependant on location and local weather. Solar radiance measurements consist of global and/or direct radiation measurements taken periodically throughout the day. The measurements are taken using either a pyranometer (measuring global radiation) and/or a pyrheliometer (measuring direct radiation). In well-established locations, this data has been collected for more than twenty years.
2. Solar insolation
While solar irradiance is most commonly measured, a more common form of radiation data used in system design is the solar insolation. The solar insolation is the total amount of solar energy received at a particular location during a specified time period, often in units of kWh/(m2 day). While the units of solar insolation and solar irradiance are both a power density (for solar insolation the "hours" in the numerator are a time measurement as is the "day" in the denominator), solar insolation is quite different than the solar irradiance as the solar insolation is the instantaneous solar irradiance averaged over a given time period. Solar insolation data is commonly used for simple PV system design while solar radiance is used in more complicated PV system performance which calculates the system performance at each point in the day. Solar insolation can also be expressed in units of MJ/ m² per year.
Consider solar radiation when designing your system
In PV system design it is essential to know the amount of sunlight available at a particular location at a given time. Ensure that the solar service provider you engage with is able to provide you with a system design that takes solar radiation into account…
We're launching the second volume of our much-anticipated Solar & Back-Up Power catalogue next month. Be among the first to receive it, straight to your inbox. Click here to REGISTER your interest now!