How certain are you that you’re being billed accurately for your electricity consumption?
In this article, we compare smart meters to analogue meters. We outline the working principle of a smart meter, and discuss their pros and cons for both the consumer and the electric utility.
What are meters used for?
An electric meter is used to measure how much electricity is being consumed in a residential or commercial building. It provides data on the amount of electricity consumed to power the lights, heating and cooling systems or any electrical device installed in your home or facility. These meters can either be an analogue meter or a digital “smart” meter.
Electrical power usage is measured in kilowatt hours (kWh). A kilowatt hour represents the consumption of 1000 watts in one hour of time. The electricity bill you receive every month is calculated by multiplying the amount of electricity consumed and the tariff rate.
Analogue Meters
An analogue electrical meter is a device that is useful for monitoring electricity usage on a periodic basis, as well as checking the accuracy of electric bills monthly. The device consists of running dials that are best read by trained personnel. The purpose of the device is to indicate how much electricity has been used since the previous reading. Representatives from the electric utility or municipality will have to take monthly readings to determine your electricity consumption.

Smart Meters
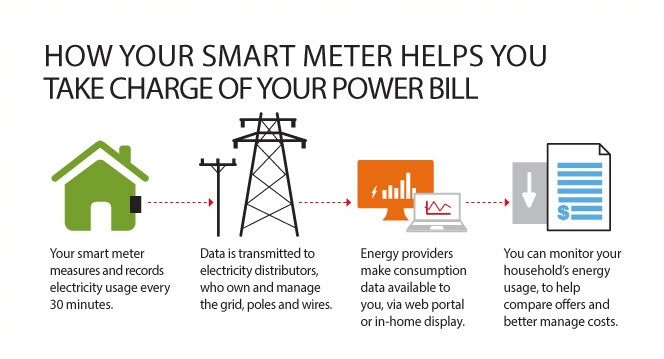
A smart meter is an interactive and multifunctional device, compared to an analogue meter. It performs the function of recording electricity use daily, and shares the information between electricity suppliers and consumers. This sharing of information is conducted over wireless frequency networks. A smart meter used for a home energy management system allows for an advanced metering infrastructure to be created with supporting interactive devices. This system manages energy consumption. For example, a smart meter can be programmed to reduce the electricity consumed during non-peak hours, reducing costs in the future.
How Does a Smart Meter Work?
A smart electricity meter operates by measuring the voltage and electrical current flow at regular intervals. Using this data, it then adds up the power consumed in 30-minute intervals. This information is then sent to your in-home display and to your electricity supplier. Different communication technologies are used in different kinds of premises. For example, a Home Area Network (HAN) is used to communicate with your in-home display, whilst a different technology will be implemented to allow a Wide Area Network (WAN) to send data to and from the communications company.
Apart from measuring energy, the meter is also able to constantly monitor its own performance and environment. An example of this, is that in the event of the meter having an internal memory problem or if the terminal cover has been removed, then the meter will report it. The supplier will then send someone to resolve the problem after contacting you.
Advantages of Smart Meters for Consumers
- More accurate readings can be obtained as the risk of human error would be removed.
- A smart meter allows for a far greater and a more detailed feedback regarding energy use.
- It enables the consumer to adjust their habits so that they can reduce their electricity bill.
- The use of a smart meter will assist in highlighting faulty appliances. As it indicates the usage at any time, it will allow you to notice any sudden spikes in electricity that could be associated with a faulty appliance. Therefore, identifying these promptly will ensure that the fault is dealt with quickly and safely.
Disadvantages of Smart Meters for Consumers
- An increase in cost for the installation of a new meter.
- There are privacy concerns for the personal data that is collected and how it will be used.
- The consumer has an increase in responsibilities for the meter.
Advantages of Smart Meters for Electric Companies
- The use of it will eliminate manual monthly meter readings.
- Monitors the electrical system in real time.
- The use of the meter will encourage more efficient use of power resources.
- It assists in providing more responsive data for the balancing of electric loads whilst reducing blackouts.
- It allows for dynamic pricing.
- The use of the device will allow for the optimization of profit with existing resources.
Disadvantages of Smart Meters for Electric Companies
- An electrical company will incur an additional cost to train personnel, develop equipment and implement new processes for data storage.
- The company will have to manage public reaction and feedback concerning new meters.
- Making a long-term financial commitment to new hardware/software.
- Ensuring the security and privacy of metering data.
RESOURCES:
Click HERE to learn about Net Metering
Click HERE to view Schneider's Power Monitoring demo site (Username & Password: demo)
Need a smart metering solution? CHAT to us!

