In this NEW series, we will be taking you through the ins and outs of circuit breaker technology.
Part one of the series shares a basic understanding of what circuit breakers are, how they work and how they compare to fuses.
In Part two below, we get into the detail of circuit breaker components.
Watch this space to catch the full series!
What does a circuit breaker comprise of?
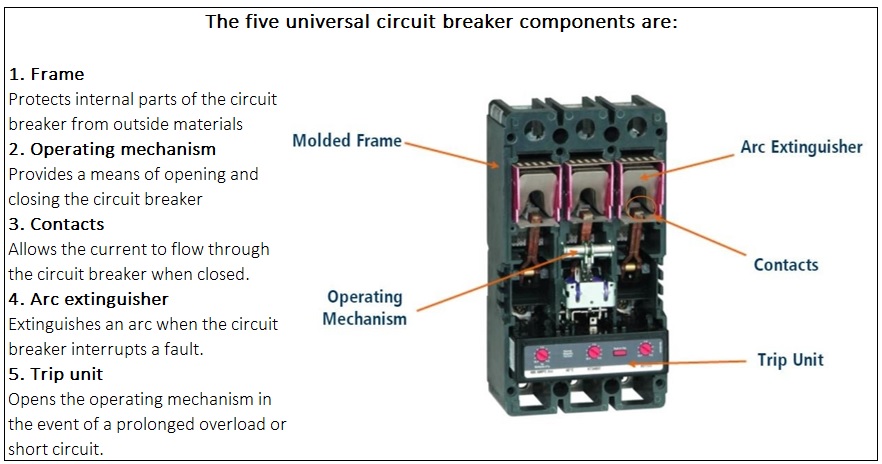
Although low and medium voltage circuit breakers have unique designs that are specific to amperage, voltage and application, there are five main components that are universal across the different types of circuit breakers.
1. Frames
The circuit breaker frame provides the rigidity and strength required to successfully deal with the interruption process and achieve the desired interrupting ratings. It insulates and isolates the electrical current in order to protect people and equipment during use or operation. Frames can be made from metal or molded insulating materials.
Metal Frame
A metal frame is assembled from precise metal pieces that are bolted and welded together to form the frame.
Molded Case
Molded case frames are made from strong insulating materials such as glass-polyester or thermoset composite resins (plastic frames).
2. Operating Mechanism
There are two types of operating mechanisms, over toggle and two step stored energy.
Over Toggle
The function of the operating mechanism is to provide a means of opening and closing the circuit breaker. This toggle mechanism is the quick-make, quick-break type, meaning that the speed with which the contacts snap open or close is independent of how fast the handle is moved.
In addition to indicating whether the breaker is ON or OFF, the operating mechanism handle indicates when the breaker is tripped by mobbing to a position midway between the ON and OFF.
Two Step Stored Energy
The two-step stored energy mechanism is used when a large amount of energy is required to close the circuit breaker and when it needs to close rapidly. The major advantages of this mechanism are rapid reclosing and safety. Rapid reclosing is achieved by storing charged energy in a separate closing spring. Safety is achieved by providing remote charging of the spring.
The two-step stored energy process is designed to charge the closing spring and release energy to close the circuit breaker. It uses separate opening and closing springs. This is important because it permits the closing spring to be charged independently of the opening process. This allows for an open-close-open duty cycle.
3. Contacts
Contacts are found in the arc interruption chamber (in low voltage circuit breakers) and in the vacuum interrupter (in medium voltage vacuum circuit breakers). The contact assembly consists of the movable contact, the movable contact arm, the stationary contact and the stationary conductor. As the circuit breaker opens or closes, the fixed contact moves to close (make) or open (break) the circuit.
The contacts are designed to protect against two fault conditions:
1. Overcurrent (thermal overload)
2. Short Circuit (magnetic)
4. Arc Extingusher
An arc is a discharge of electric current crossing a gap between two contacts. Arcs are formed when the contacts of a circuit breaker open due to larger than normal current. Arcing is a condition that must be dealt with quickly and effectively by a circuit breaker. The ability of the circuit breaker to control the arc is key to its short circuit interrupting capability. An arc extinguisher is the component of the circuit breaker that extinguishes an arc when the contacts are opened. Circuit breakers must be designed to control them because arcs cannot be prevented.
5. Trip Unit
The function of a trip unit is to trip or open the operating mechanism in the event of a prolonged overload or short circuit fault condition such as thermal overload, short circuit currents and specialty faults. To accomplish this, an electromechanical or a solid state trip unit is provided.
Electromechanical trip units utilize bimetals and electromagnets to provide overload and short circuit protection and do not include any specialty protection such as ground fault. They are commonly used in low voltage circuit breakers.
Electronic trip units offer capabilities such as programming monitoring diagnostics communications system coordination and testing that are not available on thermal magnetic trip units.
Source:
Click HERE to learn more about circuit breakers.
Need a solution for your facility? CHAT to us now!