Employing a condition monitoring system in your facility can ensure the reliability of your operations. How? By implementing processes to monitor your equipment, you can ensure machine up-time, the reduction in consequential damage to machinery, and the improvement of the overall operational efficiency.
In this NEW series, we introduce you to condition monitoring.
In Part 1, we start by reviewing the various benefits of a condition monitoring system, the commonly used techniques and the different types of condition monitoring systems that are implemented.
In Part 2 and Part 3, we unpack vibration monitoring. We progress in the series with Part 4 – an over view of motor circuit analysis. We end the series with Part 5 - residual current monitoring.
What is Condition Monitoring?
Considering that unexpected faults or shutdowns can result in production loss, or even a fatal accident, a process must be implemented to mitigate these. Condition monitoring is a system of continuously monitoring operational characteristics of a machine. It is put in place to predict the need of maintenance, before machinery deterioration or a breakdown can occur. A condition monitoring system provides information about the machine, to pre-empt failures thus reducing downtime. Information such as the vibrations in a machine, its operating temperature or condition of its oil is recorded.
What are the most common methods for Condition Monitoring?
1. Trend Monitoring
This involves the continuous, regular measurement and interpretation of data. A suitable and measurable indication of machine or component deterioration must be selected. By studying these trends, one can determine when deterioration goes over the critical limit.
For example, airplane engine data can be tracked to detect and diagnose abnormalities in engine performance, leading to the prevention of significant damage.
2. Condition Checking
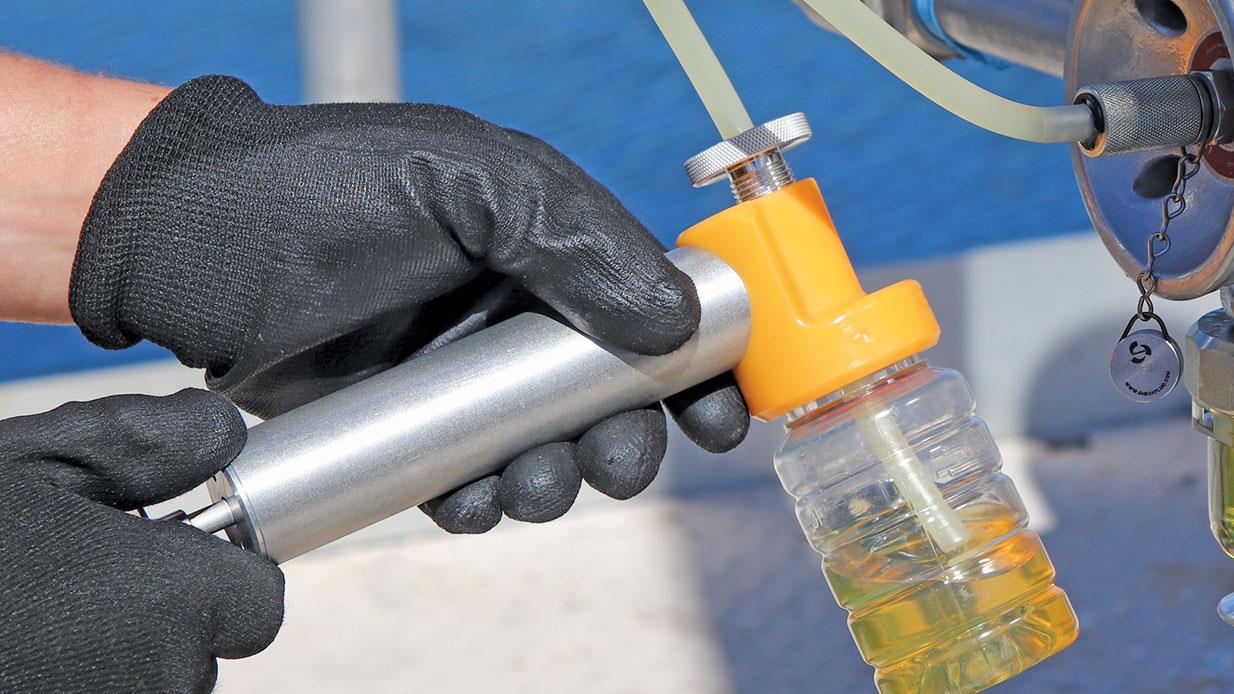
This method involves taking measurements periodically using an appropriate indicator, whilst the machine is in operation. This information is used to measure the condition of the machine at any given time. Consider the example of the use of an oil sight glass in order to check the condition of a machine’s lubricant in real time.
What are the Advantages of Condition Monitoring?
Condition monitoring outputs data in real time enabling the user to determine the root cause of a problem faster. The use of wireless technology on the equipment also connects employees with real time data by using smart phones or tables. The use of this system also enables the plant to go from a reactive approach to a predictive maintenance program, thus showcasing the health of the equipment without the need of additional labour.
In sum, the advantages of Condition Monitoring include:
- Reduction in maintenance costs
- Reduced downtime
- Extension of the asset life
- Cost savings on prematurely changed resources
Are there any disadvantages of Condition Monitoring?
The downside of implementing a condition monitoring system is, unfortunately, the cost. Sensors, necessary tools, and the labour costs involved in installing the system result in an increase in expenditure. An added cost to train employees to use the equipment accurately and effectively must also be considered. The use of sensors in a harsh environment will also lead to them being damaged and requiring replacement more than anticipated.
What Condition Monitoring Techniques are currently used?
The conditions below are the most common techniques used presently to monitor machinery.
1. Vibration Analysis
This process is implemented to measure and monitor the vibration level and frequencies of a machine. Vibration analysis allows for the detection of machine imbalance, bearing failures, mechanical looseness, misalignment, resonance and natural frequencies, electrical motor faults, bent shaft and cavitation. Estimations indicate that vibration warnings can provide a lead time of 3 months before a failure can happen.
2. Acoustic Emissions
Acoustic emissions are an aspect of vibration analysis, but at a higher frequency than those detected during a typical vibrational analysis. Monitoring these high frequency signals allows for the detection of cracking or impact.
3. Infrared Thermography
It is a process that uses a thermal imager to detect radiation that is emitted from an object. The radiation is then converted to a temperature, and the temperature distribution is displayed on an image. The process is used to monitor electrical and mechanical conditions of motors, bearings, refractory insulation and the locating of gas, liquids, and sludge levels. Abnormal heat patterns found within a machine could indicate an inefficiency or a defect.
4. Ultrasound Testing
This process is useful for high pressure fluid situations and both low and high-speed mechanical applications. The shock pulse method is commonly used for condition monitoring. It is a technique that uses signals emitted from rotating bearings as the baseline for efficient monitoring of machines.
5. Motor Circuit Analysis
This is a de-energized low voltage test method that assesses the health of the motor and the associated cabling. Performing motor circuit analysis on a set schedule can reduce downtime in your plant and increase the lifespan of your electrical motor.
6. Oil Analysis
This process involves analysing the health of machinery lubricants, oil contamination and wear. The process also includes moisture analysis, particle counting, elemental analysis, and acid/base numbers, measuring viscosity and using Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy to determine other parameters.

What are the Different Condition Monitoring Types?
The 3 different condition monitoring types are:
1. Offline Condition Monitoring
This type of monitoring is used on assets that are less critical, and where periodic scanning is sufficient to determine the state of the equipment. Offline conditional monitoring is often implemented using both vibrational and oil analysis.
2. Online Condition Monitoring
Online condition monitoring involves the continuous measurement of an asset by connecting machine-mounted sensors to system software wirelessly. It allows for real-time warnings, obtained from either vibrational analysis, acoustic emissions, ultrasound, or infrared thermography, to be sent out to the respective employees.
3. Route-Based Condition Monitoring
This is a technique that is employed when a technician records data intermittently using a handheld device. It is a method that is used to create a trend pattern and determine if an advanced analysis is required.
From the above, it is clear that implementing a conditional monitoring system in your plant will increase up-time, increase the lifespan of equipment, and result in a reduction in consequential damage. Follow part 2 and 3 in the series to learn more!
Considering the implementation of such a system in your facility, and not quite sure where to start?
CHAT to us!


